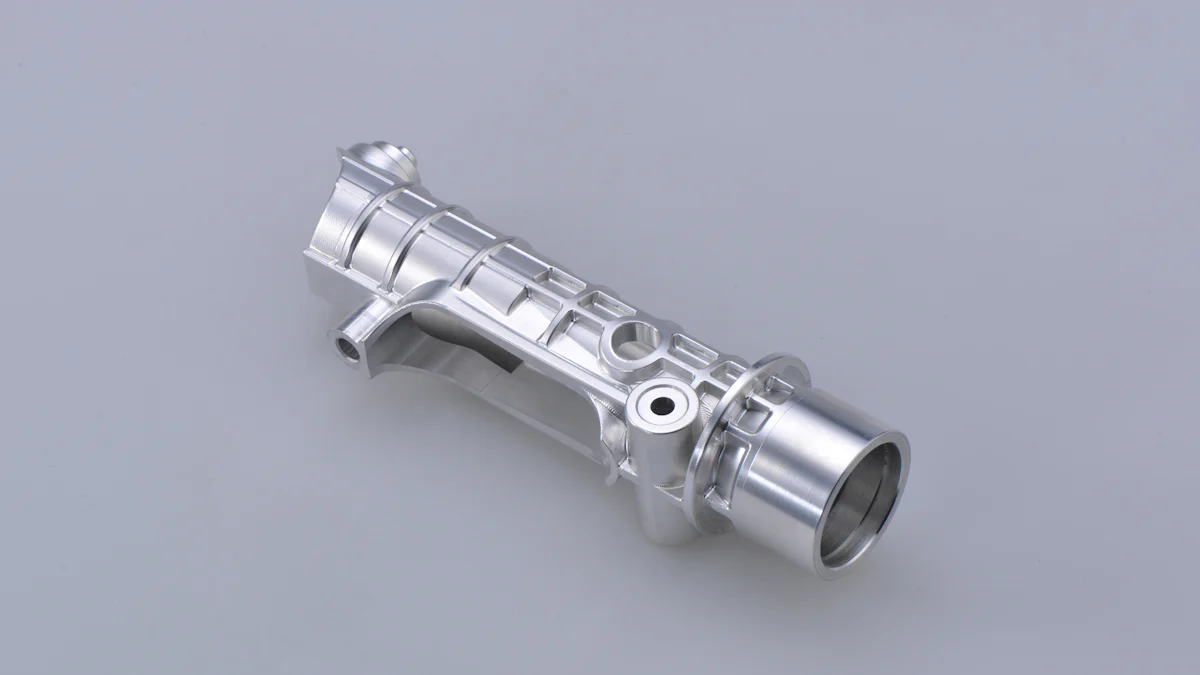
The exhaust system plays a vital role in a car’s performance and environmental impact. The exhaust manifold, as the first component in this system, collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders and directs them to the exhaust pipe. Understanding how the exhaust manifold works is crucial for maintaining engine efficiency and reducing emissions.
What is an Exhaust Manifold?
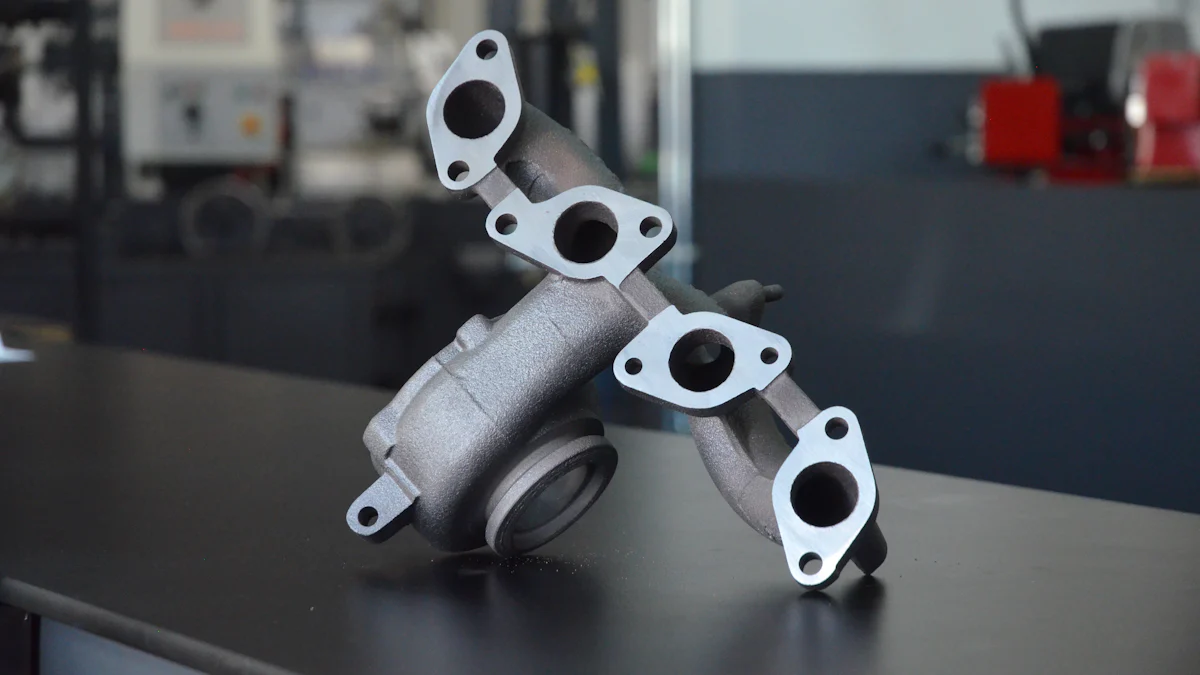

Definition and Purpose
Basic Definition
An exhaust manifold is a crucial component in a car’s exhaust system. It collects exhaust gases from multiple engine cylinders and directs them to the exhaust pipe. This process ensures that harmful gases exit the vehicle efficiently.
Purpose in the Exhaust System
The primary purpose of the exhaust manifold is to channel exhaust gases away from the engine. By doing so, it helps maintain optimal engine performance and reduces harmful emissions. The manifold also aids in heat management by dissipating the high temperatures generated during combustion.
Types of Exhaust Manifolds
Cast Iron Manifolds
Cast iron manifolds are common in many vehicles. These manifolds are durable and can withstand high temperatures. The cast iron construction provides excellent heat resistance, making these manifolds reliable for long-term use.
Stainless Steel Manifolds
Stainless steel manifolds offer improved performance and longevity. These manifolds resist corrosion and provide better heat dissipation compared to cast iron. Stainless steel manifolds are often used in high-performance vehicles due to their superior durability.
Performance Manifolds
Performance manifolds, also known as headers, are designed to enhance engine output. These manifolds optimize exhaust gas flow, reducing back pressure and improving engine efficiency. Performance manifolds are typically made from high-quality materials like stainless steel or special alloys. These manifolds often feature a ceramic coating for additional heat resistance.
How Does an Exhaust Manifold Work?
Collection of Exhaust Gases
From Engine Cylinders
The exhaust manifold collects gases from the engine cylinders. Each cylinder releases exhaust gases after combustion. The manifold gathers these gases efficiently. This process ensures that harmful gases do not linger in the engine.
Directing to the Exhaust Pipe
The exhaust manifold directs the collected gases to the exhaust pipe. This step is crucial for maintaining a smooth flow of exhaust gases. The manifold channels the gases away from the engine. This direction helps in reducing back pressure, which can affect engine performance.
Heat Management
Heat Dissipation
The exhaust manifold plays a vital role in heat dissipation. The manifold absorbs and disperses the high temperatures generated during combustion. This heat management prevents overheating of the engine components. Efficient heat dissipation also prolongs the lifespan of the manifold.
Impact on Engine Performance
Proper heat management by the exhaust manifold impacts engine performance positively. High temperatures can damage engine parts. The manifold’s ability to manage heat ensures optimal engine function. This management helps in maintaining the engine’s efficiency and reliability.
Emission Control
Role in Reducing Emissions
The exhaust manifold contributes significantly to emission control. The manifold collects and directs exhaust gases efficiently. This process reduces the amount of harmful emissions released into the environment. Effective emission control helps in complying with environmental regulations.
Integration with Catalytic Converter
The exhaust manifold integrates seamlessly with the catalytic converter. The manifold directs gases to the converter for further processing. This integration ensures that harmful gases get converted into less harmful substances. The combined effort of the manifold and converter reduces overall vehicle emissions.
Common Issues with Exhaust Manifolds
Cracks and Leaks
Causes of Cracks
High thermal stress often causes cracks in the exhaust manifold. The constant heating and cooling cycles weaken the material over time. This weakening can lead to the development of cracks. Poor design or manufacturing defects can also contribute to this issue.
Symptoms of Leaks
Exhaust leaks manifest through various symptoms. A noticeable drop in engine performance often indicates a leak. Unusual noises, such as hissing or tapping sounds, may also occur. Visible exhaust fumes under the hood can signal a leak. A burning smell often accompanies these symptoms.
Warping
Causes of Warping
Warping occurs due to uneven heating and cooling. High temperatures cause the metal to expand. Rapid cooling then leads to contraction. This cycle can distort the shape of the exhaust manifold. Improper installation or poor-quality materials can exacerbate warping.
Detection and Repair
Detecting warping requires a visual inspection. Look for any signs of distortion or misalignment. A warped exhaust manifold can cause gasket failures. Repairing warping often involves resurfacing the manifold. In severe cases, replacement may be necessary.
Gasket Failures
Importance of Gaskets
Gaskets play a crucial role in sealing the exhaust manifold. These components prevent exhaust gases from leaking. Proper sealing ensures optimal engine performance. Gaskets also help in maintaining emission control standards.
Signs of Gasket Failure
Gasket failures present several signs. A decrease in engine efficiency often indicates a problem. Increased exhaust noise can also signal a gasket issue. Visible soot around the gasket area suggests a leak. A burning smell may accompany these symptoms.
Maintenance and Repair Tips
Regular Inspections
What to Look For
Regular inspections of the exhaust manifold help maintain engine performance. Look for visible cracks or leaks. Check for unusual noises, such as hissing or tapping sounds. Inspect for any signs of soot or burning smells around the manifold area. These symptoms often indicate potential issues.
Frequency of Inspections
Conduct inspections of the exhaust manifold at least twice a year. More frequent checks may be necessary for high-performance or older vehicles. Regular inspections help detect problems early, preventing costly repairs.
Professional Repairs
When to Contact a Mechanic
Contact a mechanic if there are visible cracks or leaks in the exhaust manifold. Unusual noises or a burning smell also warrant professional attention. Mechanics have the expertise and tools to diagnose and repair manifold issues effectively.
Cost Considerations
Repair costs for an exhaust manifold vary based on the extent of damage. Minor repairs, such as gasket replacements, are relatively inexpensive. Major repairs, like fixing cracks or replacing the manifold, can be more costly. Investing in timely repairs prevents further damage and higher expenses.
DIY Maintenance
Basic Maintenance Tips
Performing basic maintenance on the exhaust manifold helps prolong its lifespan. Regularly clean the manifold to remove soot and debris. Ensure that bolts and gaskets are secure. Avoid using harsh chemicals that may damage the manifold material.
Tools Required
Basic tools for maintaining the exhaust manifold include a socket set, torque wrench, and cleaning brush. A flashlight helps inspect hard-to-see areas. Having a repair manual specific to the vehicle model provides valuable guidance.
The exhaust manifold plays a crucial role in a car’s exhaust system by collecting and directing exhaust gases. Regular maintenance and timely repairs ensure optimal engine performance and reduce harmful emissions. Professional help should be sought for any visible cracks, leaks, or unusual noises. Proper care of the exhaust manifold enhances vehicle efficiency and longevity.
Post time: Jul-23-2024



